Animal Cell Model: Understanding the Basics of Cellular Structure
The study of cells is fundamental to understanding life itself, and the animal cell model serves as a crucial tool in this pursuit. By replicating the intricate structure of animal cells, scientists and educators gain valuable insights into cellular functions and processes.
Importance of Animal Cell Models in Science
Animal cell models play a pivotal role in scientific research, allowing scientists to study cellular behavior, disease mechanisms, drug interactions, and much more in a controlled environment.
Learn about the functions of the nucleas, cell wall, membrane etc
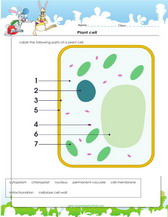
Learn to label the parts of a plant in this pdf worksheet, pdf printable for kids.
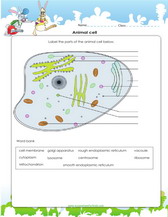
Learn to label parts of a cell and learn about cell characteristics
Learn to label the parts of a plant in this pdf worksheet, pdf printable for kids.
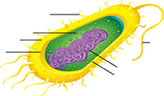
Basic Structure of an Animal Cell
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell, essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance within the cell where organelles are suspended. It provides support and facilitates cellular processes.
Nucleus
The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material, DNA, and is responsible for regulating gene expression and controlling cellular activities.
Organelles Within an Animal Cell
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing energy through cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, with rough ER studded with ribosomes and smooth ER involved in detoxification and lipid synthesis.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus processes and packages proteins synthesized in the cell, directing them to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, translating mRNA into amino acid sequences to form proteins.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down waste materials, foreign substances, and cellular debris.
Centrosome
The centrosome plays a crucial role in cell division, organizing microtubules during mitosis and meiosis.
Creating an Animal Cell Model
Creating an animal cell model is an engaging and educational activity that helps students grasp the complex structure of cells.
Materials Required
- Styrofoam ball (representing the cell)
- Modeling clay (for organelles)
- Paints or markers (for labeling)
- Toothpicks or craft sticks (for attaching organelles)
- Reference materials (diagrams or textbooks)
Step-by-step Procedure
- Begin by painting or coloring the Styrofoam ball to resemble the cell membrane.
- Mold various colors of modeling clay into shapes representing different organelles.
- Attach the organelles to the cell membrane using toothpicks or craft sticks, positioning them accurately according to their functions.
- Label each organelle with its name and function using paints or markers.
- Once complete, display the model and use it as a visual aid for learning about animal cell structure.
Importance of Animal Cell Models in Education
Animal cell models serve as invaluable educational tools, providing students with a hands-on approach to learning about cellular biology and fostering a deeper understanding of complex concepts.
Applications of Animal Cell Models in Research
Animal cell models are utilized in various fields of research, including medicine, pharmacology, genetics, and biotechnology, to study diseases, test drug efficacy and safety, and advance scientific knowledge.
Animal cell models play a crucial role in various areas of research, including biomedical, pharmaceutical, and basic biological studies. Here are some key applications:
-
Drug Discovery and Development : Animal cell models are used to screen and test potential drugs for efficacy and safety. By exposing these cells to different compounds, researchers can assess their effects on cellular processes, toxicity levels, and potential side effects. This helps in identifying promising drug candidates and understanding their mechanisms of action.
-
Disease Modeling : Animal cell models are utilized to mimic various human diseases, such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and genetic disorders. By manipulating cellular conditions or introducing specific genetic mutations, researchers can study disease mechanisms, identify biomarkers, and test potential therapeutic interventions.
-
Toxicity Testing : Animal cell models are employed to assess the toxicity of chemicals, environmental pollutants, and consumer products. By exposing cells to these substances, researchers can evaluate their adverse effects on cellular functions, such as cell viability, proliferation, and metabolism. This aids in regulatory decision-making and the development of safer products.
-
Stem Cell Research : Animal cell models, particularly stem cells derived from various sources, including embryonic, induced pluripotent, and adult stem cells, are valuable tools for studying developmental processes, tissue regeneration, and disease modeling. These cells offer insights into cell differentiation, tissue engineering, and potential therapies for degenerative diseases.
-
Viral Pathogenesis Studies : Animal cell models are utilized to investigate the pathogenesis of viral infections and develop antiviral strategies. By infecting these cells with viruses, researchers can study viral replication, host immune responses, and mechanisms of viral evasion. This knowledge aids in the development of vaccines, antiviral drugs, and diagnostic tools.
-
Cellular Signaling and Physiology : Animal cell models are used to study cellular signaling pathways, intracellular communication, and physiological processes. By manipulating signaling molecules or genetic pathways within these cells, researchers can elucidate complex cellular interactions, regulatory mechanisms, and responses to external stimuli.
-
Gene Editing and Functional Genomics : Animal cell models serve as platforms for gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, enabling the precise modification of genetic sequences. This facilitates the study of gene function, identification of disease-associated genes, and development of potential gene therapies.
-
Bioproduction and Biotechnology : Animal cell models are utilized in bioproduction processes to manufacture recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and other biopharmaceuticals. These cells can be engineered to express specific proteins of interest and cultured in bioreactors to produce large quantities of biotherapeutics.
Overall, animal cell models provide valuable tools for understanding cellular processes, modeling diseases, developing therapeutics, and advancing biomedical research across diverse fields. Their versatility and relevance make them indispensable in modern scientific investigations.
Limitations of Animal Cell Models
While animal cell models offer many benefits, they also have limitations, such as lacking the complexity of living organisms and being unable to fully replicate physiological conditions in vivo.
Future Perspectives
Advancements in technology and biotechnology are continually improving animal cell models, enhancing their accuracy, reliability, and relevance to real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
In conclusion, animal cell models play a crucial role in both education and scientific research, providing insights into cellular structure and function that are essential for advancements in various fields. By understanding the basics of cellular biology through animal cell models, we can unlock new discoveries and innovations that benefit society as a whole.
FAQ Section
-
Are animal cell models only used in educational settings?
- No, animal cell models are also extensively utilized in scientific research for studying diseases, drug testing, and various other applications.
-
Can animal cell models fully replicate the complexity of living organisms?
- While they offer valuable insights, animal cell models have limitations in replicating the full complexity of living organisms due to their simplified nature.
-
What are some common materials used to create animal cell models?
- Common materials include Styrofoam balls, modeling clay, paints or markers, and reference materials such as diagrams or textbooks.
-
How are organelles attached to the cell membrane in an animal cell model?
- Organelles can be attached using toothpicks or craft sticks, ensuring they are positioned accurately according to their functions.
-
What is the significance of labeling organelles in an animal cell model?
- Labeling organelles helps reinforce learning by associating their names and functions with their visual representations, aiding in comprehension and retention.