Block mountain diagram game quiz online
Play this game and learn the parts of a block mountain through a diagram.
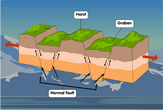 A fault-block (or “block”) mountain is formed when a single block of land is split apart into several smaller blocks due to tectonic forces in a fault. The energy released from movement near a fault can cause nearby land blocks to be raised or even tilted. Fault-block mountains refer to the portion of the block that has been raised higher, relative to the surrounding land. These elevated parts are also called horsts.
A fault-block (or “block”) mountain is formed when a single block of land is split apart into several smaller blocks due to tectonic forces in a fault. The energy released from movement near a fault can cause nearby land blocks to be raised or even tilted. Fault-block mountains refer to the portion of the block that has been raised higher, relative to the surrounding land. These elevated parts are also called horsts.
The splitting apart of the surface also forms valleys and depressions known as grabens, which help to make nearby horsts stand out more. Perhaps the most well-known examples of these types of mountains can be found in the United States. The Sierra Nevada mountain range in the state of California is composed of a series of fault-block mountains. Other examples include the Teton Range in Wyoming and the Harz mountain range in Germany. The tension in these blocks can sometimes cause horsts to topple or tilt, forming stacks of rock. As a result, many block mountains can appear incredibly steep from one side, and gentle and sloping from another perspective. Feel free to make use of our
block mountain diagram
to improve your understanding on how different mountain types are formed depending on the nature of various geological processes.
Parts of a block mountain diagram
-
The base of the mountain is the foundation on which the mountain rests. It is typically composed of solid rock and is buried deep beneath the surface of the earth.
-
The flanks of the mountain are the sides of the mountain. They are the sloping areas that extend from the base of the mountain to the summit.
-
The summit of the mountain is the highest point on the mountain. It is the top of the mountain and is often the most rugged and difficult part of the mountain to reach.
-
The slopes of the mountain are the inclined portions of the mountain. They are the parts of the mountain that are inclined at an angle and are usually covered in vegetation.
-
The valleys of the mountain are the low-lying areas between mountains. They are often shaped like a U and are usually surrounded by mountains on three sides.
-
The peaks of the mountain are the highest points on the mountain's ridge or crest. They are often the most rugged and difficult parts of the mountain to reach and may be covered in snow and ice.
-
The plateaus of the mountain are flat areas on top of the mountain. They are often surrounded by steep cliffs and are usually covered in vegetation.
-
The cliffs of the mountain are steep, vertical faces of the mountain. They are often very high and may be difficult to climb.
-
The ridges of the mountain are the long, narrow, elevated areas that run along the top of the mountain. They are often rocky and may be covered in snow and ice.
-
The valleys of the mountain are the low-lying areas between mountains. They are often shaped like a U and are usually surrounded by mountains on three sides.
Questions and Answers about block mountains
Here are some questions and answers about block mountains:
Q: What are block mountains? A: Block mountains are mountains that have been formed by tectonic plates colliding and pushing up the earth's surface. They are characterized by a series of flat, horizontal layers of rock that have been uplifted and tilted by tectonic forces.
Q: How are block mountains formed? A: Block mountains are formed when tectonic plates collide and push up the earth's surface, creating a series of flat, horizontal layers of rock that are uplifted and tilted by tectonic forces.
Q: What is an example of a block mountain? A: The Rocky Mountains in the western United States are an example of a block mountain range.
Q: What are some features of block mountains? A: Some features of block mountains include cliffs, valleys, plateaus, and peaks. They may also have steep slopes and rugged terrain.
Q: What is the highest block mountain in the world? A: The Himalayas, which are a range of block mountains located in Asia, are the highest block mountains in the world. The highest peak in the Himalayas is Mount Everest, which stands at an elevation of 29,029 feet (8,848 meters).
