Diagram of fold mountain game quiz online
Review with a diagram of a fold mountain to lable. Interactive online quiz.
 A mountain is quite the imposing landform – millions of tons of rocky material stacked like heaps, dominating the view for tens of kilometres and providing a great place for picnicking, hiking, and other activities. The fresh air, peaceful surroundings, and closeness to nature also entice many people to live on these landforms. Mountains also show Earth’s geological processes at work - specifically plate tectonics, or the slow movement of plates composing the lithosphere.
A mountain is quite the imposing landform – millions of tons of rocky material stacked like heaps, dominating the view for tens of kilometres and providing a great place for picnicking, hiking, and other activities. The fresh air, peaceful surroundings, and closeness to nature also entice many people to live on these landforms. Mountains also show Earth’s geological processes at work - specifically plate tectonics, or the slow movement of plates composing the lithosphere.
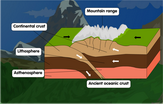
Many of the Earth’s mountains are part of a category called a ‘fold’ mountain. As two particular plates push against each other, such as in the case with convergent plate boundaries, they can force rocky material on the surface upward into a bunch of folds. Some of the planet’s most famous mountain ranges are made of fold mountains, from the tall peaks of the Himalayas to the snowy Alps of Central Europe. Not all of these mountains are folded the same, though. Their slopes might face the same direction (monocline), or its rock layers can be stacked in a zig-zagging pattern (chevron). You can review your knowledge of plate tectonics and the geological processes that form the Earth’s mountains with the help of our
diagram of a fold mountain
.
Characteristics of fold mountains
Fold mountains are some of the most spectacular and imposing geological features on Earth. They are formed when tectonic plates collide, causing the Earth's crust to buckle and fold, resulting in the creation of towering peaks and deep valleys. These mountains are characterized by their distinctive folding pattern, with the rocks and sediments being pushed up and over each other to form the peaks and valleys.
There are several types of fold mountains, including anticlines, synclines, and monoclines. Anticlines are mountain ranges that have a series of peaks, with the rock layers being folded upward in an arch-like shape. Synclines are the opposite of anticlines, with the rock layers being folded downward in a trough-like shape. Monoclines are mountain ranges that have a single steep slope, with the rock layers being tilted in one direction.
The process of fold mountain formation is complex and involves a number of different forces. The most important force is the movement of tectonic plates, which are the massive slabs of rock that make up the Earth's crust. When two tectonic plates collide, the denser plate is forced beneath the other, a process known as subduction. As the plates continue to collide, the rocks and sediments that make up the crust are subjected to tremendous pressures and temperatures, causing them to fold and deform.
The type of fold mountain that is formed depends on the type of plate collision that takes place. If the plates are moving towards each other in a convergent manner, the resulting mountain range will be a fold mountain. If the plates are moving away from each other in a divergent manner, the resulting mountain range will be a rift valley. If the plates are moving alongside each other in a transform manner, the resulting mountain range will be a fault-block mountain.
There are several well-known examples of fold mountains around the world, including the Himalayas, the Andes, and the Rocky Mountains. The Himalayas are perhaps the most famous fold mountain range, with some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest, which stands at a staggering 8,848 meters (29,029 feet) above sea level. The Andes are the longest fold mountain range in the world, stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) along the western coast of South America. The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America, running from British Columbia in Canada to New Mexico in the United States.
Fold mountains are home to a wide variety of plant and animal life, with many species being found only in these isolated mountain ranges. The harsh climate and rugged terrain of these mountains have led to the evolution of unique species that are adapted to the extreme conditions. Many of these species are threatened by habitat loss and other human activities, making it important to protect and preserve these mountains for future generations.
Fold mountains also have a significant impact on the global climate and weather patterns. The high altitude of these mountains causes the air to cool, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation. The mountains also act as a barrier, blocking cold air from the north and warm air from the south, resulting in the creation of different climatic zones on either side of the range.
In conclusion, fold mountains are some of the most iconic and impressive geological features on Earth, formed by the collision of tectonic plates and the folding of the Earth's crust. These mountains are home to a wide variety of plant and animal life and have a significant impact on the global climate and weather patterns. They are a testament to the power and majesty of the natural world, and it is important that we work to protect and preserve these mountains for future generations.
Questions and Answers About Fold Mountains
- What are fold mountains?
- Fold mountains are mountain ranges formed when tectonic plates collide and the Earth's crust folds, resulting in the creation of peaks and valleys.
- What are the different types of fold mountains?
- The different types of fold mountains include anticlines, synclines, and monoclines. Anticlines are mountain ranges with a series of peaks, synclines are mountain ranges with trough-like valleys, and monoclines are mountain ranges with a single steep slope.
- What causes the formation of fold mountains?
- The formation of fold mountains is caused by the movement of tectonic plates, which are massive slabs of rock that make up the Earth's crust. When two plates collide, the denser plate is forced beneath the other, causing the rocks and sediments to fold and deform.
- What are some examples of fold mountain ranges?
- Some examples of fold mountain ranges include the Himalayas, the Andes, and the Rocky Mountains.
- How do fold mountains impact the global climate and weather patterns?
- The high altitude of fold mountains causes the air to cool, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation. The mountains also act as a barrier, blocking cold air from the north and warm air from the south, resulting in the creation of different climatic zones on either side of the range.
